祝贺本课题组刘芬在Environ. Sci. Technol期刊中发表了一篇综述
Metal-Based Ionic Liquids in Oxidative Desulfurization: A Critical Review
Fen Liu, Jiang Yu*, Abdul Basit Qazi, Li Zhang, and Xueke Liu
Cite this: Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 3, 1419–1435
Publication Date:January 12, 2021
https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.0c05855
Copyright © 2021 American Chemical Society
Abstract
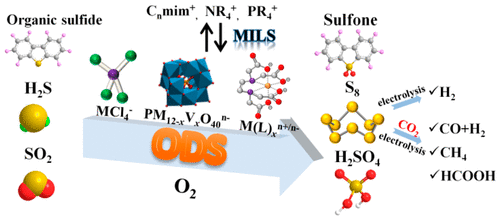
Ionic liquids (ILs) as novel functional desulfurization materials have attracted increasing attentions. Metal-based ionic liquids (MILs) are classified into three types of metal chloride ILs, metal oxide ILs, and metal complex ILs based on the definition and basic structure of MILs in this critical review. On the basis of the properties of ILs such as structure designability, super dissolution performance, good thermal and chemical stability, nonflammability, and wide electrochemical window, MILs exhibit unique advantages on hydrophobicity, oxidation performance, and Brönsted–Lewis acidity. Therefore, MILs possess both the absorption and oxidation centers for the intramolecular adsorption and oxidation to improve the oxidative desulfurization (ODS) process. During the novel nonaqueous wet oxidative desulfurization process (Nasil), H2S can be oxidized into elemental sulfur with hydrophobic MILs, which can be regenerated by oxygen for recycle, to solve the problems of low sulfur capacity, low sulfur quality, and severe secondary pollution in the aqueous Lo-Cat wet oxidative desulfurization process. Another outstanding feature of MILs in ODS is biomimetic catalysis, which has the function of activating molecular oxygen and improving the oxidation performance. Metal oxide ILs and metal complex ILs are used in combination with hydrogen peroxide or oxygen with the existing water to generate a Fenton-like reaction to convert hydrophobic organic sulfur or SO2 into hydrophilic sulfoxide/sulfone or sulfur acid, respectively. However, the corrosion of Cl– to the equipment and emulsification phenomenon in the extraction process of sulfoxide/sulfone separation still need further study. Furthermore, the promising strategies to construct highly efficient and green desulfurization processes for large-scale applications are provided.
The Supporting Information is available free of charge at https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.est.0c05855.
Table S1: Characterization of properties and structure of metal chloride ILs. Table S2: Characterization of properties and structure of metal oxide ILs. Table S3: Characterization of properties and structure of metal complex ILs. Table S4: Oxidative desulfurization of organic sulfide in metal chloride ILs over the past decade. Table S5: Oxidative desulfurization of organic sulfide in metal oxide ILs over the past decade. Table S6: Oxidative desulfurization of organic sulfide in metal complex ILs over the past decade. Table S7: Oxidative desulfurization of H2S in MILs over the past decade. (PDF)
